Nonlinear Noise2Noise for Efficient Monte Carlo Denoiser Training
Andrew Tinits and Stephen Mann
SIGGRAPH Asia 2025 Conference Papers
 Paper (arXiv)
Paper (arXiv)
Paper (official)
Slides (Keynote)
Slides (PowerPoint)
Pretrained Models (coming soon)
Summary
We show that nonlinear functions can be safely applied to the noisy targets in Noise2Noise training to achieve practical benefits without adding significant bias. We demonstrate our method on a Monte Carlo denoising task, where our results approach those of clean references, but are produced using only noisy training data.
Abstract
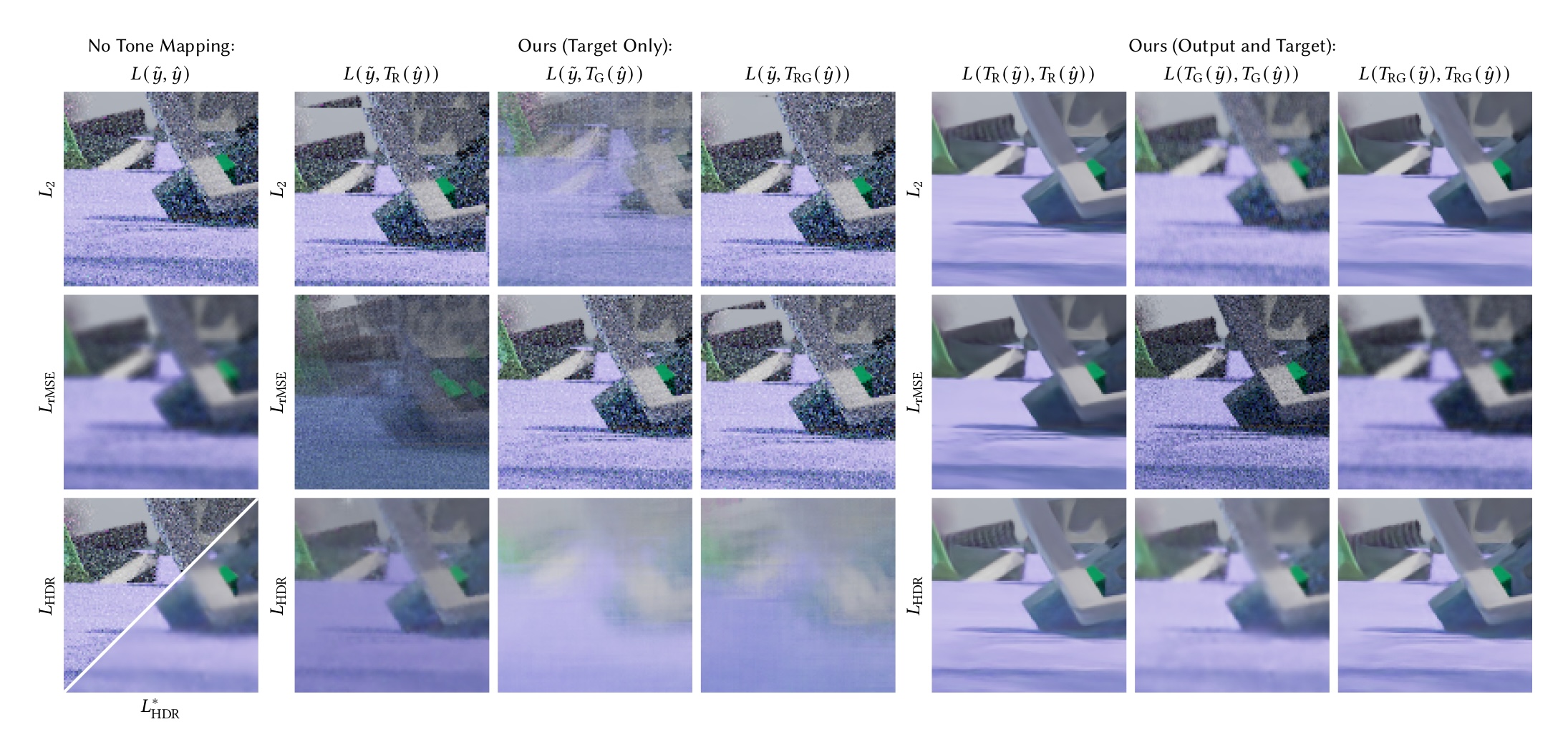
The Noise2Noise method allows for training machine learning-based denoisers with pairs of input and target images where both the input and target can be noisy. This removes the need for training with clean target images, which can be difficult to obtain. However, Noise2Noise training has a major limitation: nonlinear functions applied to the noisy targets will skew the results. This bias occurs because the nonlinearity makes the expected value of the noisy targets different from the clean target image. Since nonlinear functions are common in image processing, avoiding them limits the types of preprocessing that can be performed on the noisy targets. Our main insight is that certain nonlinear functions can be applied to the noisy targets without adding significant bias to the results. We develop a theoretical framework for analyzing the effects of these nonlinearities, and describe a class of nonlinear functions with minimal bias.
We demonstrate our method on the denoising of high dynamic range (HDR) images produced by Monte Carlo rendering, where generating high-sample count reference images can be prohibitively expensive. Noise2Noise training can have trouble with HDR images, where the training process is overwhelmed by outliers and performs poorly. We consider a commonly used method of addressing these training issues: applying a nonlinear tone mapping function to the model output and target images to reduce their dynamic range. This method was previously thought to be incompatible with Noise2Noise training because of the nonlinearities involved. We show that certain combinations of loss functions and tone mapping functions can reduce the effect of outliers while introducing minimal bias. We apply our method to an existing machine learning-based Monte Carlo denoiser, where the original implementation was trained with high-sample count reference images. Our results approach those of the original implementation, but are produced using only noisy training data.
BibTeX
@inproceedings{10.1145/3757377.3763931,
author = {Tinits, Andrew and Mann, Stephen},
title = {Nonlinear Noise2Noise for Efficient Monte Carlo Denoiser Training},
year = {2025},
isbn = {9798400721373},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3757377.3763931},
doi = {10.1145/3757377.3763931},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the SIGGRAPH Asia 2025 Conference Papers},
articleno = {49},
numpages = {11},
keywords = {Noise2Noise, nonlinear functions, Jensen gap, Monte Carlo denoising, high dynamic range, tone mapping},
series = {SA Conference Papers '25}
}
Contact
The paper and slides are licensed under CC BY 4.0.
Questions and comments are welcome at amtinits (at) uwaterloo (dot) ca.